Nowadays, enabling HTTPS on our websites is an inevitable practice. It helps secure the visitors’ sensitive data being sent/received while navigating the website. This is crucial to limit the threats to online users when visiting insecure HTTP websites.
To implement HTTPS, website owners need to issue an SSL/TLS certificate. Obtaining such certificates used to be difficult and expensive. However, it’s getting much easier and cheaper with the available automated and free certificate providers.
Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL are certificate authorities that provide totally free SSL/TLS certificates for HTTPS connections. Let’s Encrypt is much more common than ZeroSSL but it has limited capabilities. ZeroSSL comes in multiple free/paid versions, one of which is almost identical to Let’s Encrypt.
We review and compare both certificate authorities in terms of prices, certificate issuing and validity, limits and renewals, technical support, and many other aspects. Then, we help website owners decide which certificate provider would fit their needs.
Here is our summary of the comparison between Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL:
Since we do our best to share high-quality content, this post may contain affiliate links that earn us a commission if you act upon clicking on them (i.e. signup, subscribe, make a purchase, etc.). This doesn’t, by any means, impact the experience of our readers.
| Let’s Encrypt | ZeroSSL | |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Certificate Authority (CA) | Certificate Authority (CA) |
| Certificate Type | Domain Validation (DV) | Domain Validation (DV) |
| Website | https://letsencrypt.org | https://zerossl.com |
| Logo | ||
| Launch | 2014 / 2015 | 2016 |
| Funding | Sponsorships & Donations (Non-profit) | Subscription (Paid Plans) |
| Certificate Issuing | ACME only | Online, ACME, REST API |
| Price | Free | Free / Paid |
| Certificate Validity | 90 days | 90 days / 1 year |
| Domain Verification | DNS, File Upload | DNS, File Upload, Email |
| Rate Limit | 50 Certificates per Week/Domain | No Limit / Specific Limit (per plan) |
| Multi-Domain Certificates | Supported | Supported (per plan) |
| Wildcard Certificates | Supported | Supported |
| Technical Support | Not Available | Available (per plan) |
| ACME Automation | Supported | Supported |
| Remote API | Not Available | Available (per plan) |
| User Interface | Not Available | Available |
1. SSL/TLS Certificates
SSL/TLS certificates are protocols to encrypt data between web servers and web clients (browsers). Primarily by using encrypted HTTPS connections.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is the successor of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), and both are used interchangeably with HTTPS certificates.
Types of SSL/TLS Certificates
Depending on the type of domain they are securing, there are three main types of SSL/TLS certificates:
Domain Validated (DV) Certificates: this is the simplest type of SSL/TLS certificate, it covers basic websites like personal sites, blogs, small online stores, and online portfolios.
Both Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL provide Domain Validated certificates.
Organization Validated (OV) Certificates: this type provides an advanced level of encryption and is suitable for medium-sized businesses and online platforms. Issuing a certificate of this type usually requires submitting an application to validate the ownership of the domain and the identity of the organization.
Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: this type represents the highest standard of security and encryption. It covers advanced businesses and financial organizations that deal with very sensitive visitor information.
2. What is Let’s Encrypt?
Let’s Encrypt is a non-profit certificate authority that is run for the public’s benefit and served by the Internet Security Research Group (ISRG). It provides totally free TLS certificates to encrypt communications with websites and protect users’ exchanged data. This initiative aims at helping eliminate un-secure HTTP protocols and move towards fully encrypted HTTPS websites.
Nowadays, Let’s Encrypt certificates are undoubtedly the most commonly used for HTTPS websites. According to their stats, they serve over 300M websites on the internet.
To maintain it as a free solution to secure the internet, Let’s Encrypt is funded by some of the major entities in the digital world, including Mozilla, Google Chrome, Cisco, Meta, and AWS.
Let’s Encrypt was the first to provide free certificates for website owners using HTTPS. Before that, obtaining paid certificates was the only reliable way to issue a dedicated domain validation SSL certificate for the website.
3. What is ZeroSSL?
ZeroSSL is another certificate authority to create and manage SSL/TLS certificates for websites. It is sometimes seen as the first alternative to Let’s Encrypt in terms of providing free SSL/TLS certificates.

The project started in 2016, and it currently issues more than 1M certificates on monthly basis. The initial purpose was to facilitate installing free 90-Day SSL certificates issued by third-party vendors. Later on, it became a stand-alone certificate authority to issue and validate SSL certificates.
Although ZeroSSL provides free certificates similar to Let’s Encrypt, it comes with advanced features to manage and monitor the issued certificates. However, some of them are only included in paid subscription services.
Besides ZeroSSL, SSLForFree.com used to be another provider of free certificates. SSLForFree.com has become part of ZeroSSL since May 2020. So that their certificates are now issued by ZeroSSL as well.
4. ZeroSSL vs Let’s Encrypt: What is the Difference?
We provide a detailed comparison between the two authorities in terms of certificate issuing, pricing, validity, and many other aspects.
4.1. Certificate Issuing
Initially, to understand how certificates can be issued, it’s useful to describe the idea of ACME protocol.
ACME (Automatic Certificate Management Environment) is a communication protocol to automate interactions between certificate authorities and web servers. Most hosting providers such as Bluehost and Hostinger do provide built-in tools that use ACME protocols to automate issuing and validating HTTPS certificates. So website owners don’t need to manually issue and install SSL certificates for their websites.
Although Let’s Encrypt provide helpful online documentation, they don’t have any means to obtain certificates directly from their website. The only possible way to issue/renew a Let’s Encrypt certificate is via tools that use ACME protocol (which usually runs on the domain host).
Accordingly, to get a certificate from Let’s Encrypt, website owners need to demonstrate control over the website domain. This means if you don’t have access to your domain’s control panel, you will mostly require support from the server admin to issue and verify (see domain verification) an HTTPS certificate.
On the other hand, ZeroSSL provides three possible means to issue HTTPS certificates:
- ZeroSSL website: where they provide an interface to issue and manage certificates. Here, website owners can obtain an HTTPS certificate and verify it (see domain verification) directly on the ZeroSSL website.
- ZeroSSL ACME Automation: this method is similar to Let’s Encrypt. Where website owners who have access to their domain control panel are able to order and renew certificates automatically using the ACME integration.
- ZeroSSL REST API: where subscribers to specific plans can create certificates using dedicated API (see API Automation).
With that the case, both authorities allow issuing certificates via ACME. Let’s Encrypt has no other options, while ZeroSSL has online purchases and an API as well.
4.2. Pricing
As a non-profit organization, Let’s Encrypt doesn’t aim at making income from the certificates they issue. For this reason, all Let’s Encrypt certificates are totally free of charge.
On the other hand, ZeroSSL works a little bit differently, as they provide both free and paid certificates. It’s just like a commercial service with free plans/options.
Thus, the pricing plans for ZeroSSL vary depending on the features package and how certificates are obtained.
ZeroSSL prices for certificates obtained from the website
ZeroSSL website provides multiple plans for users who want to have HTTPS certificates with advanced features. Paid plans come with subscription fees that can be paid monthly or yearly at different rates.
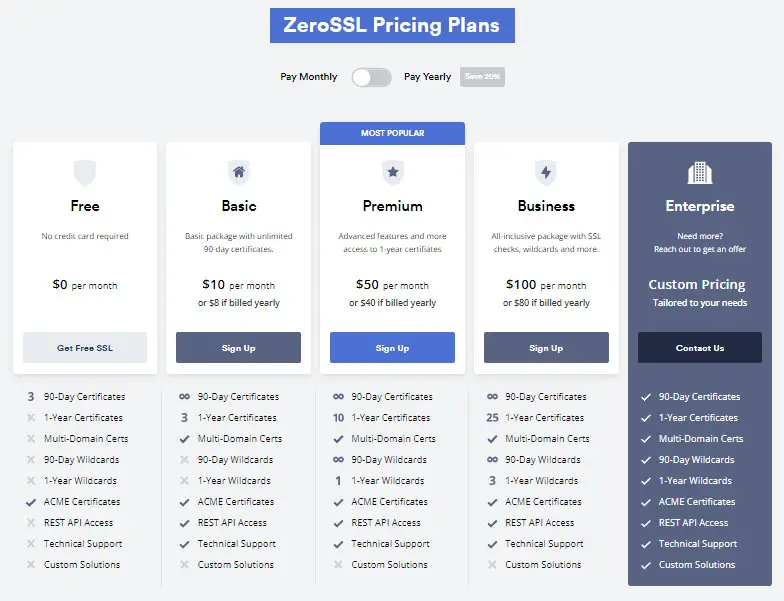
Among the available plans, there is a Free subscription which is limited to a maximum of 3 certificates with 90-day validity each. This means the free-of-charge plan ends after 3 x 90-Day issuings/renewals, then the Basic plan starts to apply.
The Free plan here is like an experimental period for users who are willing to upgrade to advanced packages with premium features and support.
ZeroSSL prices for certificates obtained via ACME
This model works pretty similarly to Let’s Encrypt. Using the automated integration, website owners will be able to obtain unlimited 90-day ZeroSSL certificates free of charge. This means certificates can be issued and renewed via ACME at no extra cost.
That being said, both Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL provide totally free certificates via ACME.
4.3. Validity
Both Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL certificates are valid for a limited time. They have no options (neither free nor paid) to obtain a lifetime HTTPS certificate.
Let’s Encrypt certificates are usually valid for 90 days, but they can be regularly renewed at no extra charge.
ZeroSSL has two validity options: 90-Day (free/paid) certificates and 1-Year (paid) certificates. The free 90-Day certificate can be also automatically renewed (via ACME) for free.
This means both Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL certificates issued via ACME are 90-Day valid and can be renewed free of charge.
4.4. Domain Verification
In order to properly install HTTPS certificates, website owners need to verify their ownership of the domain for which they issued a certificate. This is usually done in multiple ways, mostly by uploading a file provided by the certificate authority.
Let’s Encrypt has two ways to prove domain ownership: by using DNS (CNAME) records and by uploading a file to the server. In many cases, this will be done automatically when issuing the certificate using the built-in automated tool in the web hosting.
Either way, the website owner has to have control over the domain control panel to install and verify Let’s Encrypt certificates.
For ZeroSSL, both DNS (CNAME) and File Upload are also options to verify domain ownership. Furthermore, ZeroSSL has an additional feature to allow users to validate domain ownership via email.
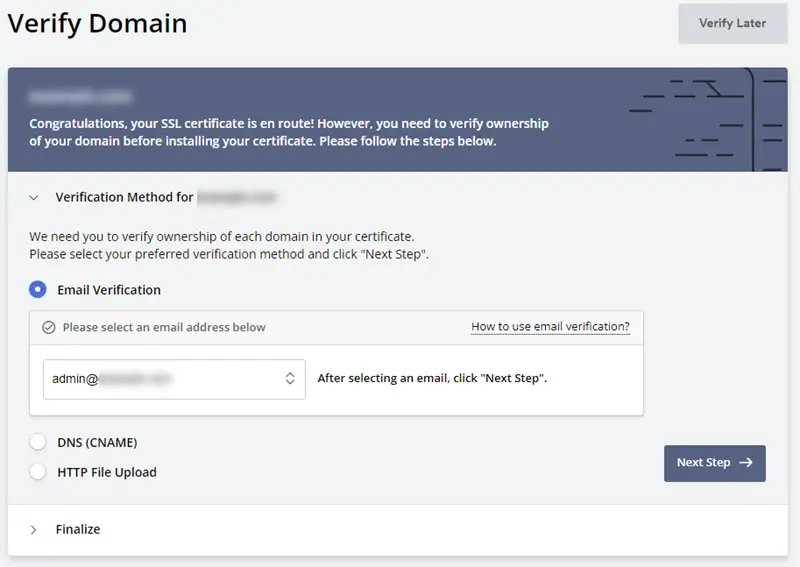
That said, website owners won’t need to access the domain control panel or contact the server admin to install their certificate. As they just need to have a valid admin email under the same domain.
4.5. Rate Limits
Although Let’s Encrypt allows issuing and renewing an unlimited number of certificates, it does apply some kind of rate limits to ensure fair usage for their users.
The main limit Let’s Encrypt applies is 50 certificates per domain per week. There are some other limits but all of them are pretty high and mostly enough to work for most people.
For ZeroSSL, the maximum number of certificates varies depending on the issuing channel. The free plan on the website allows issuing/renewing a maximum of three 90-Day certificates. While in paid plans users are able to issue an unlimited number of 90-Day certificates as well as multiple 1-Year certificates as per each plan.
On the other hand, ZeroSSL certificates automatically obtained via ACME are unlimited and there is no rate limit like the one applied to Let’s Encrypt certificates. This is one of the main differences between Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL certificates.
4.6. Multi-Domain Certificates
Typically, each SSL/TLS certificate covers and validates one specific domain. A Multi-Domain SSL certificate is one certificate that contains several different domain names. Usually using the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) mechanism.
Let’s Encrypt supports Multi-Domain certificates in its issued certificates. ZeroSSL also has Muli-Domain options for both 90-Day and 1-Year certificates in both free ACME and paid certificates. The free plan on the website is the only one that doesn’t support Multi-Domain certificates.
4.7. Wildcard Certificates
Wildcard SSL/TLS certificates are used to secure both the domain name and its subdomains in one certificate. It is different from Multi-Domain certificates that secure multiple domain names in one certificate. Wildcard certificates are usually generated by adding an asterisk (*) to the beginning of the domain name.
Both Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL support Wildcard possibilities in all their issued certificates. Regardless of the certificate validity, type, or subscription plan.
4.8. Technical Support
In spite of the automated SSL/TLS integration that comes with most web hosting providers, installing and renewing HTTPS certificates might run into many technical and communication issues. Here is where technical support comes into play.
As a free and simple solution, Let’s Encrypt relies on automation to keep costs down. Thus, they don’t offer direct technical support to their subscribers. Instead, users might benefit from their useful documentation and community support forums to find answers to the most common questions.
On the other side, as a proprietary solution, all paid plans of ZeroSSL do provide technical support to their customers. However, users can also benefit from their help center or contact them for further support.
4.9. API/ACME Automation
As mentioned earlier, both Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSS do have full ACME compatibility to issue and renew SSL/TLS certificates automatically and free of charge. This makes it very easy to obtain and renew HTTPS certificates for a website directly from inside the hosting control panel.
Additionally, unlike Let’s Encrypt, ZeroSSL also provides REST APIs that support remote certificate creation, validation, renewal, and management. The ZeroSSL website provides full documentation of the available APIs and their features. However, note that the API access is only available for paid subscription plans.
4.10. User Interface
As a simple solution to issue HTTPS certificates, Let’s Encrypt doesn’t provide a place to manage issued certificates. ACME is the main interface to deal with Let’s Encrypt certificates.
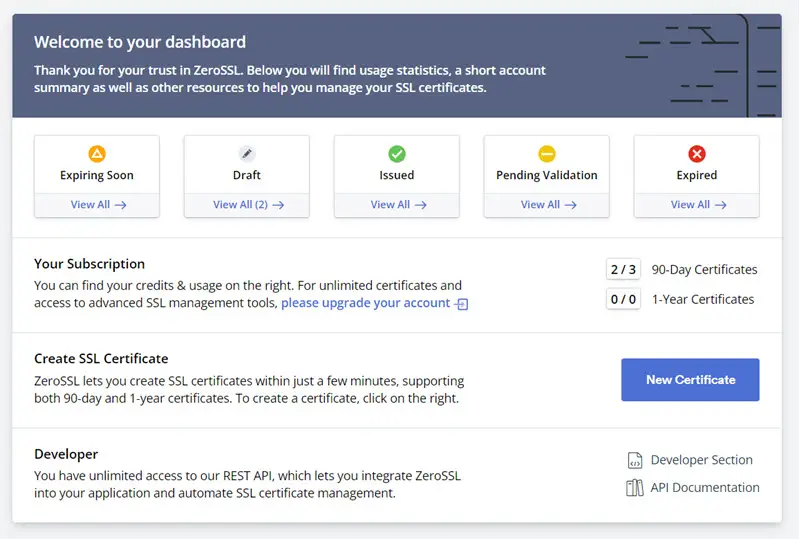
On the other hand, ZeroSSL has an intuitive user interface to take care of and manage obtained certificates and issue new ones. The online dashboard classifies certificates as per their status, along with providing quick actions to create new certificates and manage subscription details.
5. ZeroSSL vs Let’s Encrypt: What to Choose?
With all the mentioned details, it’s obvious that the automated version of ZeroSSL is almost identical to Let’s Encrypt. Both issue automated certificates using ACME, and these certificates are free, renewable, and can be issued to an unlimited number of domains.
Let’s Encrypt is the most common certificate authority for HTTPS websites and its popularity surpasses ZeroSSL. However, what actually makes the difference is what ZeroSSL provide in their paid subscription plans.
ZeroSSL is a freemium alternative to Let’s Encrypt!
That being said, if you are looking for a basic HTTPS certificate to secure your blog, portfolio, or basic website without any additional features, then Let’s Encrypt would be an adequate choice. The automated version of ZeroSSL might be a suitable alternative as well.
Otherwise, ZeroSSL is a better solution if your work requires higher levels of customer trust. Which needs sophisticated management tools to manage multiple HTTPS certificates. This includes custom solutions, technical support, longer validity, account management, and API integrations. ZeroSSL also has an Enterprise plan for custom solutions that don’t fit into other offered plans.
For more details about other available free SSL certificate providers, you can refer to our article about free alternatives to Let’s Encrypt.

Free SSL Certificates: 4 Alternatives to Let’s Encrypt [Compared]
In this article, we present and compare the top 5 free SSL/TLS certificate providers in terms of cost, validity, limits, and other details.
Nonetheless, if you are running an organization, an advanced e-commerce platform, or a financial institution then you need to consider other types of Organization Validation (OV) or Extended Validation (EV) certificates.


