Retrieving the most up-to-date information is quite important to find the best and most relevant answer to our search query. Some web pages make it clear when the page content was originally created or last updated. While the majority of the digital content on the internet is not timestamped.
That being said, sometimes we need some ways to check when a webpage was actually last updated. Or at least we seek an indication of when the author approximately modified the content or put it online. Particularly when this detail plays a key role in determining the validity of the obtained results.
There are many useful ways to check when a website was last updated (or created). Some of them are pretty common but don’t bring reliable results! While some others are highly trustworthy even though they don’t tell the exact age of the webpage.
We present in this article the most reliable and relatively simple ways that might help us check when a webpage was created or last updated.
Moreover, based on our experience in websites development, we assessed each method according to three factors:
- Availability: the possibility to detect a last-update date using this method.
- Accuracy: if available, how accurate the detected date is (it is close to the anticipated last modification date).
- Reliability: if available, how trustworthy the detected date is (it truly reflects the actual period when the modification was applied).
Here is our final list of methods to check when a webpage was created / last updated sorted by reliability, accuracy, and availability respectively.
| Method | Availability | Accuracy | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1- WayBack Machine by Internet Archive | Medium | Medium | High |
| 2- Content Metadata | Medium | High | Medium |
| 3- Website Sitemap | Medium | High | Medium |
| 4- Open Graph HTML Code | Medium | High | Medium |
| 5- Contacting Content Owner | Low | High | Medium |
| 6- Google Search Results | High | Medium | Medium |
| 7- HTTP Headers Last-Modified Field | High | Medium | Medium |
| 8- Context and Comments Clues | Low | Low | Medium |
| 9- Webpage URL | Low | Medium | Low |
We describe at the end of this article how we validated and assessed these methods, for more details please check our methodology.
1. WayBack Machine by Internet Archive
- Availability: Medium | Accuracy: Medium | Reliability: High
The Internet Archive is a digital library that aims at providing universal access to digital content. It contains free collections of digitized materials, such as websites, music, and books.
WayBack Machine is a free service by the Internet Archive which regularly visits and saves webpages over time. It provides a historical log of how the webpage looked the time it was visited by this machine. It also grants access to the webpage history even if the website went offline.
The most powerful side of this tool is the historical versions of the webpage. This not only tells us when the webpage was updated, but also allows us to track a specific section to know how old it is.
You just need to scan several snapshots to determine when the section was created, last modified, or removed.
Although WayBack Machine is a powerful tool, it has a couple of drawbacks when it comes to knowing the webpage’s last update time:
- Some websites might not appear in this machine at all: Which can happen for many reasons, such as the automated crawlers are still unaware of the website’s existence, or the bots are blocked or excluded by the website owner.
- Recent updates might take time to appear: This depends on the scanning frequency, so the webpage might have been changed since the last snapshot.
- There is no guarantee that every single change will be captured: The machine only shows versions when the webpage was crawled, so there might be some missing “un-crawled” versions.
With that in mind, although WayBack Machine does not provide an accurate last modified date, it is still pretty useful to give a general idea about the content age and development.
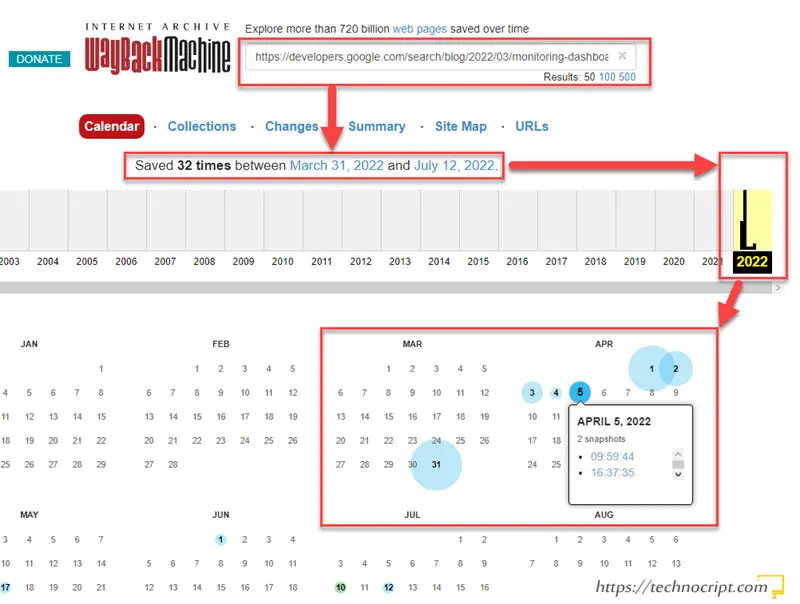
Check Update History in WayBack Machine
- Copy the webpage URL.
- Go to WayBack Machine.
- Paste the URL in the input field, then hit
Enter. - The website archive will appear. Otherwise, the URL has not been archived but you can add it for later updates.
- Select the year when you need to track the updates, then select a date from the calendar.
- Select a snapshot, then the machine will display the webpage at this time.
2. Content Metadata
- Availability: Medium | Accuracy: High | Reliability: Medium
In some cases, the webpage itself provides metadata about the content author, category, creation time, and last update time. These details usually appear somewhere next to the title, or at the beginning/end of the webpage.
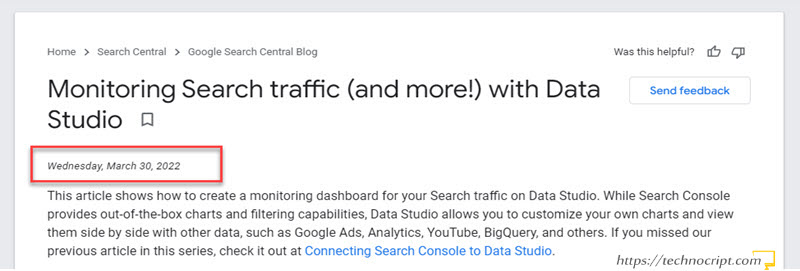
Unfortunately, these details are not always available, as they depend on many factors. Mostly, the tool or content management system the author used to create the content, and of course the author’s decision to show/hide them.
Keep in mind that even if the content clearly indicates its age, this might not be accurate or reliable. As in most cases the content creator can adjust it to any other value.
Additionally, some content creators tend to update this field to a recent date even if they applied no or tiny modifications to their content.
Check Last Updated Time in Content Metadata
- Open the webpage.
- Look for the content metadata next to the page title or at the beginning/end of the webpage.
- Find a date that appears next to
Created,Updated,Last Updated,On, or just as a plain date.
3. Website Sitemap
- Availability: Medium | Accuracy: High | Reliability: Medium
The Sitemap is a formatted document that tells information about the website, its structure, its internal pages, and other elements. It plays an important role in Search Engine Optimization to help search engines like Google crawl the website efficiently.
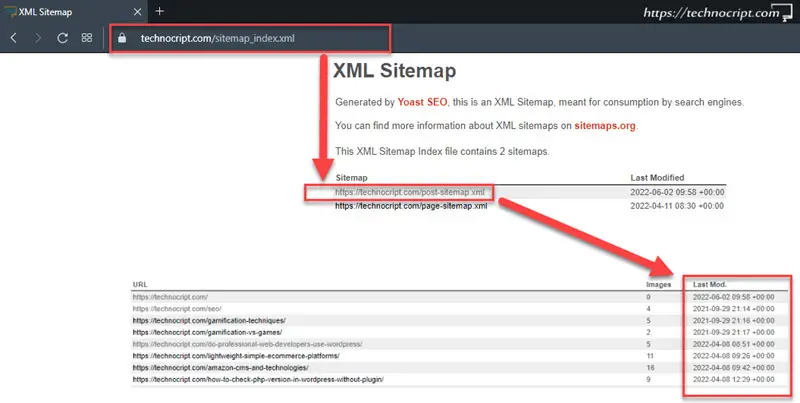
One of the details that sitemaps can tell is the last updated date of each webpage/URL.
However, the sitemap describes the full website, so there is no separate sitemap for each specific page. Accordingly, we need to browse the domain sitemap and look into it for the last updated date of the required webpage.
Some websites don’t publish a sitemap of their pages or maintain a static one that is not frequently updated. Moreover, other websites might not provide the last modified time in the sitemap.
Check Last Modified Time in Sitemap
- Open the webpage.
- Look inside the footer, top header, sidebar, or other locations for a link to the sitemap.
- If there is no link, try guessing some common sitemaps:
- Move to the webpage URL.
- Remove everything after the domain name (usually after the first
"/"). - Try typing one the of following suffixes:
sitemap.xml,sitemap_index.xml,sitemap-index.xml,sitemap.php,sitemap.txt,sitemap. Then hitEnter. - If you are still unlucky, check other ways to find the website sitemap.
- When the sitemap appears, navigate through it to find the required webpage URL (some sitemaps organize URLs based on their type, and others might have all URLs listed in one page).
- If provided, the last modified field will be listed next to the webpage URL.
4. Open Graph HTML Code
- Availability: Medium | Accuracy: High | Reliability: Medium
Open Graph or The Open Graph protocol is an internet protocol originally created by Facebook. It consists of HTML tags that add details to the webpage so that it can be properly shared on social media platforms.
Open Graph meta tags are included within the <head> section of the HTML structure. They define specific properties of the content, such as title, type, image, URL, …
There are two main tags that describe the age of the webpage:
- article:published_time: when the article was first published.
- article:modified_time: when the article was last changed.
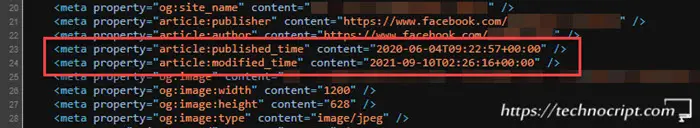
Based on the publishing tool the author used, these meta tags might be embedded in the webpage so we can simply inspect them in the page source in our browser.
Bear in mind that, just like any other HTML element, these tags can be also modified by the authoring tool.
Check Modified and Published Time in Page Source
- Open the webpage.
- Right-click on any blank area inside it.
- Choose
Page Source,View Page Source, or other similar options. If not found, click on another area. This should open the HTML page source. - Hit
CTRL+Fto open the search box, then typearticle:modified_timeorarticle:published_time. - Find the meta tags and then look for published and last modified times within the
contentattribute.
5. Contacting Content Owner
- Availability: Low | Accuracy: High | Reliability: Medium
Getting in touch with the website owner is also a possible method to know how recent the webpage is. This usually depends on two factors: knowing the owners’ contact details, and their willingness to answer our query.
Most websites do have means to contact them, usually via an email address or embedded contact form. However, there is no guarantee that our inquiry will be answered, and if so, answered accurately. Particularly for older or abandoned websites.
However, this is still an easy way to opt for in case no other solution worked out.
We provide here a generic template for contacting a website owner and asking for the last update time. You can use and modify it as you need.
Dears at [WEBSITE],
I am a [ROLE] at [COMPANY].
I am doing research about [TOPIC], and I found some pretty helpful information in your article titled [TITLE] on this link: [URL]
I need to add a reference to your article in my research, so I would like to ask you how old this webpage is and when was the last time you updated/created it, particularly this section: [SECTION START – END].
Your answer would help me provide accurate information in my research.
Many thanks in advance for your kind consideration.
Best Regards,
[YOUR NAME]
[YOUR CONTACT DETAILS]
Check Webpage Age by Contacting Website Owner
- Go to the website.
- Look in the footer, top header, or sidebar for the contact details, or find a link to the contact page. Usually named:
Contact,Contact Us,Get In Touch, … - Prepare a message asking for the webpage last modified date. Be precise, specify the URL and reason behind your request, and provide your contact to get back to you (you can use the template above).
- Send your request via the specified contact details.
- If you haven’t received any answer for a while, you can try to repeat the request one another time.
6. Google Search Results
- Availability: High | Accuracy: Medium | Reliability: Medium
Search engines like Google do their job by crawling websites on a regular basis. When a webpage is scanned by google, some additional details about the content are retrieved as well.
These meta details are then used by google to add extra information to retrieved websites on the search engine result page (SERP). This brings a richer and much better searching experience.
Therefore, when searching for a query on google, it sometimes shows a date next to the meta description of the retrieved URLs.
Unfortunately, we couldn’t find any confirmed source to know what this date actually indicates. According to multiple sources, it might indicate one of the following:
- When the page was first/last indexed by google.
- When the page was last indexed and google observed a substantial change in the content.
- A date was found and pulled from the page content (such as the Content Metadata we mentioned earlier).
- Other values relevant to the search experience.
In this video, Google’s Matt Cutts talks briefly about how google chooses these dates.
Accordingly, dates shown in google search results refer to when google thinks the retrieved content (or snippet) was created (or last modified).
Check Last Updated Date in Google Search Results
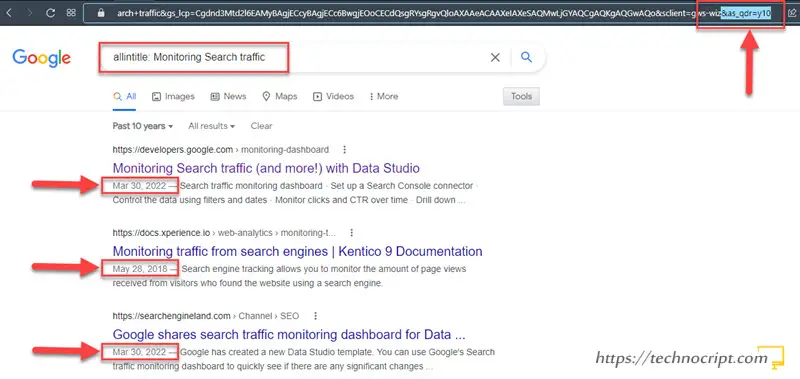
- Go to google.com.
- Search for any keyword that its results used to contain the required webpage. Alternatively, copy the webpage title and search for:
allintitle: "WEBPAGE TITLE HERE" - Find your webpage in the results.
- Find the last updated date next to its meta description.
- If the date is not shown, add
&as_qdr=y10to the end of the search results URL. This asks google to bring results from the past “10 years” and display the date for each one.
7. HTTP Headers Last-Modified Field
- Availability: High | Accuracy: Medium | Reliability: Medium
HTTP is the protocol that controls the connection between web clients and web servers. It transmits the web page we request with all its elements: HTML, CSS, images, text, etc.
HTTP Response Header is the part of the protocol that carries additional invisible but descriptive information about the webpage, such as content type and server information.
As part of this header, the server may send a field called Last-Modified which is, according to the protocol description:
HTTP Header Last-Modified indicates the date and time at which the origin server believes the variant was last modified.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol — HTTP/1.1
BUT:
The protocol also adds that the meaning of this field depends on the server implementation and the nature of the original resource.
That said, for dynamic webpages which represent the majority of modern web content, this field may be misleading. Because it may also indicate when the response was created, the page layout was changed, or the page was cached or restored from a backup; rather than the actual last update time of the content.
Thus, HTTP Headers Last-Modified field tends to be useless or inaccurate in some cases.
Anyway, as we don’t know how the requested webpage was processed, we can still resort to this field keeping in mind the mentioned caveats.
There are multiple ways to check the HTTP Headers Last-Modified field:
Check Last-Modified Field using a Free Tool
As HTTP headers usually include technical details, this is the simplest way to find the Last-Modified field:
- Copy the webpage URL.
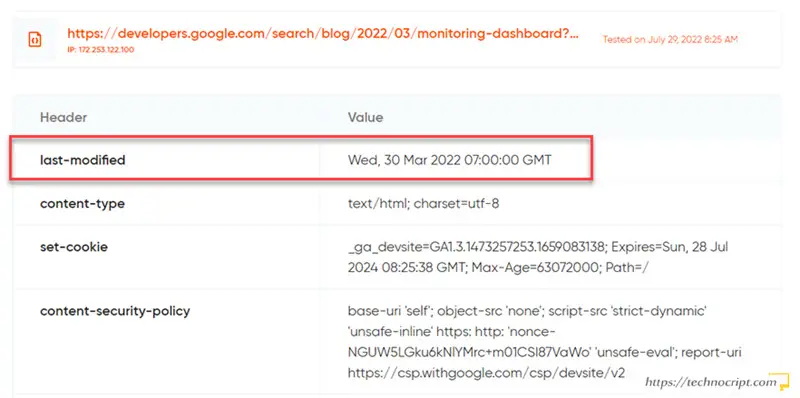
- Open GeekFlare tool: https://geekflare.com/tools/http-headers-test (or any other similar one).
- Paste the URL in the input field.
- Hit
TEST HEADERSbutton. - Find the
Last-Modifiedfield in the table.
Check Last-Modified Field using Developer Tools
This method is fairly difficult to follow by non-developers and depends on the browser. However, if you don’t prefer to rely on third-party tools for whatever reason, this method is an alternative solution:
- Open the webpage.
- Right-click on any blank area inside the webpage.
- Choose
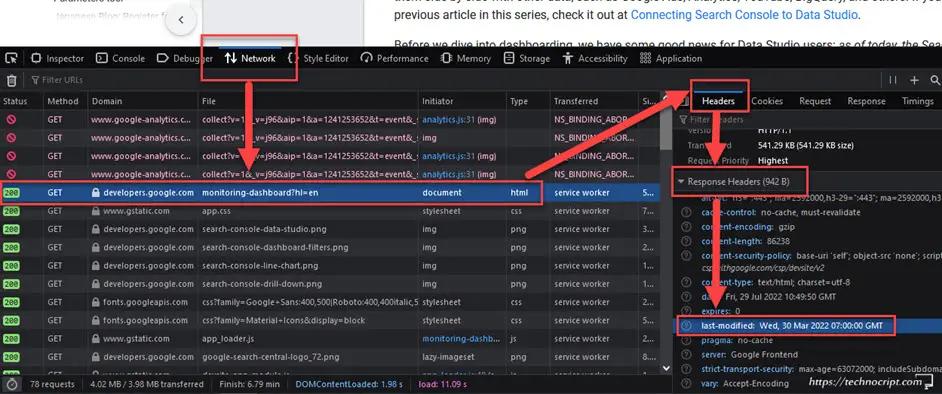
Inspect,Inspect Element, or other similar options. If not found, click on another area. - The
Developer Toolwill open. If this doesn’t work, search for how to open developer tools in your browser. - Navigate to
Networktab. - Reload the webpage (hit
F5or use the reload button in your browser). - This will load a long list of requests, find the first one that “partially” matches the webpage domain and URL.
- The request details will appear. Select
Headers, then find theLast-Modifiedvalue underResponse Headers.
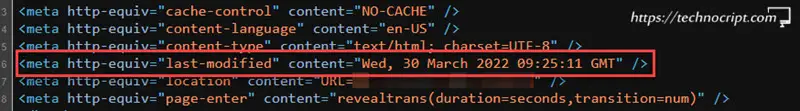
Check Last-Modified Field using HTML http-equiv Meta Tag
HTML meta tags can be used to simulate the HTTP Header response using http-equiv attribute. This is an alternative way to set HTTP Header response fields when the content owner can’t access server configurations.
<meta http-equiv="last-modified" content="Wed, 30 March 2022 09:25:11 GMT" />The attribute value to set the Last-Modified field is http-equiv="Last-Modified". However, this value is no longer valid but we can still inspect it for older websites.
- Open the webpage.
- Right-click on any blank area inside the page.
- Choose
Page Source,View Page Source, or other similar options. If not found, click on another area. This will open the HTML page source. - Hit
CTRL+Fto open the search box, then type"last-modified". - Find the meta tag and check the last modified date inside the
contentattribute.
Check Last-Modified Field using javascript:alert(document.lastModified)
JavaScript is a client-side programming language that allows visitors to interact with the webpage elements. In contrast to server-side languages, JavaScript code is loaded as part of the page content so it can be executed by the browser itself.
We can use simple JavaScript snippets to unveil some hidden information about the online document, such as the HTTP Header Last-Modified field.
IMPORTANT: While most other resources mention it as a separate method, JavaScript command is just an alternative way to find the HTTP Headers Last-Modified field.
Run JavaScript command using Page URL
- Open the webpage.
- Move to the page URL in your browser.
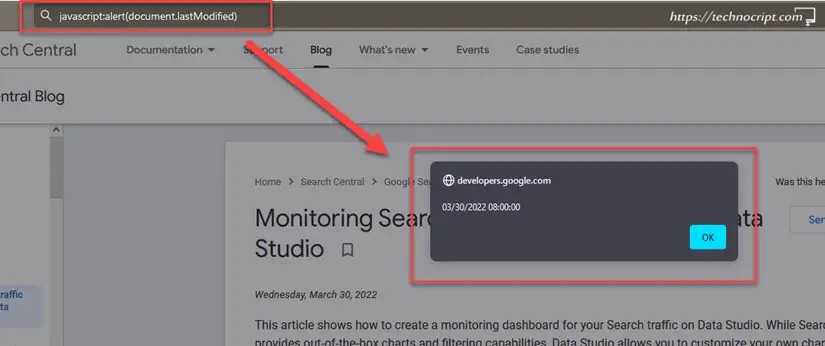
- Clear the URL and instead of it type the following command:
javascript:alert(document.lastModified) - If you copied/pasted this command, the
javascript:prefix might be omitted, so you need to retype it manually. - Hit
Enter. - A popup with the
Last-Modifieddate will appear. - If the popup didn’t appear, or the date was the current timestamp, try a different browser. If the problem persists, the webpage doesn’t have this field appended.
Run JavaScript command using Developer Tools
- Open the webpage.
- Right-click on any blank area inside the page.
- Choose
Inspect,Inspect Element, or other similar options. If not found, click on another area. - The
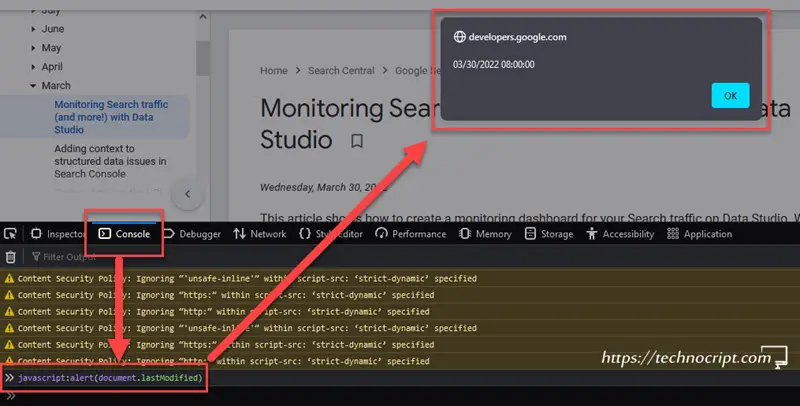
Developer Toolwill open. If not, search for how to open developer tools in your browser. - Navigate to
Consoletab. - Type the following command:
javascript:alert(document.lastModified). Some browsers ask for confirmation or show warning messages, just proceed to type this command. - A popup with the
Last-Modifieddate will appear. - If the popup didn’t appear, or the date was the current timestamp, try a different browser. If the problem persists, the webpage doesn’t have this field appended.
8. Context and Comments Clues
- Availability: Low | Accuracy: Low | Reliability: Medium
The content itself might carry some hints that help us guess when it was created or published online. Although these snippets don’t necessarily provide an accurate timestamp, we can still benefit from them to predict the approximate content age.
These clues might come in multiple forms, such as mentioning other events or referencing to specific milestones. The following are some examples of these clues:
- … last week/month/year …
- … next week/month/year …
- … yesterday/tomorrow …
- … two/three/… days/years/… ago …
- … these days …
- … recently …
Moreover, comments if enabled can also provide an approximate range of how old the webpage is. Most content management systems display the comment date and time next to it. Comments can also include time clues as well.
Any additional embedded elements or media assets such as screenshots, videos, tables, etc. may also contain helpful information to determine how old the content is.
Guess Webpage Age From Content and Comments Clues
- Open the webpage.
- Skim the content and its comments for any time references. It’s better to find multiple references.
- Check on the web for the actual dates of the referenced events.
- Try to guess the content age based on these references.
9. Webpage URL
- Availability: Low | Accuracy: Medium | Reliability: Low
Every online document has its own unique URL that specifies the resource location on the internet. The URL starts with a domain name and may contain any combination of letters or numbers to identify the resource.
Some web content management systems like WordPress come with various options for building the website URL, some of them include the webpage creation date in the URL itself.
Here are some examples of how the date may appear in URLs:
- https://www.example.com/some/key/words/19/03/22
- https://www.example.com/some/key/words/30102017
- https://www.example.com/some/key/2019/11/words
- https://www.example.com/some/key/words/13/12/18
- https://www.example.com/2021/08/some/key/words
That said, and based on how the website is managed, sometimes we can inspect the creation date in the page URL.
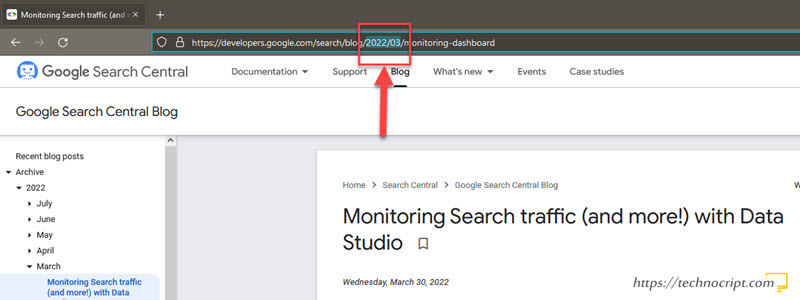
Keep in mind that in most cases this date refers to the webpage’s creation time not last update time. It can be manually modified by the content owner as well.
Check Webpage Creation Time in URL
- Go to the webpage.
- Check the webpage URL in your browser.
- Try to identify any date information in different format variations. For example
DD/MM/YYYY,MM/YYYY,MM-YY,YYYYMMDD, …
Our Methodology
When preparing this guide, we conducted deep research on all possible ways to check the webpage’s last update time. We also analyzed and tested each method manually and on multiple webpages.
Unexpectedly, we noticed that most available information is inaccurate or no longer relevant. They also don’t provide a step-by-step guide or miss some crucial details.
For example, we obtained totally different results when we applied multiple methods to the same webpage. This is primarily because each obtained last-modified field might carry arbitrary values, and some of them can be easily manipulated.
Anyway, we manually tested and validated all possible methods and sorted them based on their reliability, accuracy, and availability respectively. As it is more important to know the approximate webpage’s age even if it’s not much accurate. Rather than fetching an arbitrary value that can be manually or technically adjusted by the content owner or the hosting configurations.
Lastly, there is no confirmed way to precisely know the age of online content. As knowing these details usually requires accessing the hosting server, which is exclusively available to the content owner and the hosting company.
Conclusion
There are multiple ways to detect the last time when a webpage was modified. Some of them are quite simple, while others require some technical skills.
Regardless of the followed method, we always need to ensure the trustworthiness of the obtained last-update date. As many content management tools and hosting panels assign specific last-update values. These values don’t necessarily reflect the actual modification date. For this reason, we tried in this article to asses all methods in terms of availability, accuracy, and reliability.
Finally, we really appreciate your comment if you faced any problems when following the mentioned methods. So that we can check and reassess them in light of your feedback.


Interesting. It seems google have removed the metadata from the results when you use a time constraint on the search. I wonder why…..
Thank you Dominic for your feedback.
We checked the date again in google’s metadata for some queries and it appeared in most results!
However, as this is based on an experimental process we can’t assure the date will be available in all cases.
Great post, is there any way to find the same for first-modified or initial-modified for example when the page/post is created the first time?
Thank you ather.
You can use almost all mentioned techniques to find out when a webpage is created.
Additionally, you can sometimes find other helpful HTTP-Header fields that may reflect the post/page creation date. However, as mentioned in this article, we can’t totally rely on technical information for accurate results.
Anyway, we think the WayBack Machine is still the most reliable source to get an approximate clue of when the post first appeared on the web.